Faqs About Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Treatment

Introduction: What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine (RM) is an exciting and relatively new branch of medicine that has scientists, doctors, and patients abuzz with the excitement. As with all emerging technologies, there are many questions about regenerative medicine and/or stem cells. In this article we attempt to answer many of the most commonly asked questions on the topic. A good place to start is to first define regenerative medicine.
Medical approaches using stem cells and other natural proteins that stimulate regeneration and repair make up a branch of medicine known as RM. More specifically, RM is “the branch of medicine that develops methods to regrow, repair or replace damaged or diseased cells, organs or tissues. RM includes the generation and use of therapeutic stem cells, tissue engineering and the production of artificial organs.
Stem cells have gained a lot of notoriety over the past few decades because they are the master cells capable of differentiating (becoming more specialized) into any other cell type in the body (e.g., skin cells, liver cells, neurons, heart cells etc.). Once, differentiated they produced chemical signals including growth factors and other proteins that signal the body to regrow and heal damaged tissues. They can be safely extracted from donors or from the patient themselves, grown in a lab and transplanted back into a recipient in need. They are safe and have few ethical dilemmas now that scientists have been able to isolate stems cells from tissues from adults, not requiring cells from embryos.
FAQ’s Regarding RM and Stem Cells
-
Why are doctors and scientists so excited about RM? This is a loaded question and to fully answer this question would be the subject of many articles! But simply put there are several major reasons for excitement.
- Stems cells are a safe, natural, and effective treatment already at work in your body
- Stems cells may be able to treat diseases with no known cure by reversing damage and replacing damaged tissues and organs with viable cells
- Stems cells can lower the cost of medications since they can supplant the need for medications or work in concert with medications to speed the healing process
- Stems cells can speed recovery from surgical procedures
- Stems cells can make tissue and organ donation a thing of the past if tissues can be engineered outside of the body and not rely on donors
-
Why should I consider stem cell therapy rather than surgery? Because stem cells can differentiate into any cell type, they may be able to repair damaged tissue that might have required surgery to fix at some point. Stem cell therapies typically have little down time and pain involved making them attractive alternative for some patients.
- Will stem cell treatments regrow damaged tissue? The goal of stem cell treatment is to stimulate regrowth of existing tissues. Stem cells can function by differentiated into specialized tissues which then secrete growth factors and cytokines, chemical that affect growth, healing, and immune responses. These signals are crucial in stimulating healing and the growth of new tissue.
- How can I still benefit if my tissue growth is only mild or doesn’t occur? Yes! Let’s use osteoarthritis as an example whereby cartilage loss causes joint pain and immobility. Even if treatments do not regrow cartilage, the RM therapy decreases inflammatory cytokines, inhibits enzymatic destruction of cartilage, promotes the production of healthy synovial joint fluid, and has many other roles in promoting joint health.
- How do regenerative medicine treatments compare to steroid treatments. Steroids like cortisone are potent synthetic anti-inflammatory drugs that are only safe to administer three to four times a year due to a large range of possible side effects. In fact, steroids can even make arthritis worse as it can damage cartilage. Regenerative medicine treatments do not have any of the side effects of steroids because they are naturally found in the body and used to stimulate the body’s own healing mechanisms.
- Are these treatments legal. Stem cell treatments derived from products including Wharton’s Jelly are legal and regulated by the FDA.
- What injuries is regenerative medicine used to treat. Currently, regenerative medicine is routinely used for various orthopedic conditions including osteoarthritis. Sports injuries and other musculoskeletal conditions involving joints, tendons, and ligaments are commonly treated with various RM therapies. Many professional and armature athletes have turned to RM over surgical procedures.
- Does my age matter when I receive regenerative treatment? Yes, one’s age can play a role in determining the best treatment to receive. As we age, we produce less stem cells. Treatments like platelet-rich plasma injections are best suited for younger patients whereas, more potent stimulatory proteins like concentrated growth factors or Wharton’s jelly will have better results in older patients.
- Doe the regenerative therapy procedure hurt. Most RM therapies for joint damage involve simple injections in or around the joint space. Local anesthetics and OTC pain reliever are enough to ease any soreness from the injection. There is little to no down time and minimal pain.
- I have already had years of injections that didn’t work. How is this different? Likely, the injections you received were not designed to stimulate the body’s healing process. Most injections contain agents that serve to cushion or lubricate joints. These will not have long-term benefits whereas RM treatments are longer lasting and have the potential to stimulate healing.
- Why is Wharton’s Jelly a good source of stem cells? The umbilical cord is the site of the most concentrated levels of stem cells in any human tissue. Donated umbilical cords can be used to harvest the Jelly contain stem cells and concentrated growth factors and other therapeutic proteins.
- What are the types of Regenerative Medicine? RM therapies includes, prolotherapy, PRP (platelet-rich plasma), Wharton’s Jelly, growth factors, hyaluronic acid, and stem cell therapies.
- What is the success rate overall? The overall success rate depends on multiple factors including disease severity, the patient’s age, adherence to physical therapy program, and activity levels.
- How much do stem cell therapies cost, and does insurance cover these treatments? The cost depends on the size of the joint being treated. The average cost varies between $3000 to $5000.
- What type of doctor should administer the treatment? Doctor’s trained in the use and administration of regenerative therapies should be sought out. Most doctors have experience in orthopedics or sports medicine if joint issues are the problem. Specialists in oncology would be appropriate is cancer is to be treated.
- When would you use Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy versus BMAC? PRP is most often reserved for younger patients with mild to moderate arthritis. BMAC is more appropriate for either older patients or for moderate to severe arthritis or for tears in the rotator cuff or tendons.
- How quickly can I get back to my regular routine? After the initial injection, patients should rest the affected joint. Once the soreness subsides, physical therapy should begin. Depending on the nature of the injury, patients can resume day-to-day activities within days, but it may take a month or longer to resume strenuous activity.
- If Regenerative Medicine fails, is surgery still an option. Yes, RM in no way impacts a patient’s ability to follow up with surgery if that is needed.
- Is stem cell therapy the same as platelet-rich plasma therapy? No, PRP involves collecting platelets from the blood of the patient and reinjecting them to the site of the injury. It does not use stem cells but rather platelets which secrete therapeutic signaling proteins to stimulate healing. Stem cells are specialized cells that have the capacity to change into other cell types and have the capacity to heal or replaced damaged tissues.
- Can I drive myself home after stem cell treatment. It is likely recommended not to drive depending on the nature of your injury. For example, you may not be able to operate the car if your leg is immobilized.
If you are interested in Regenerative Medicine Therapy or have further questions not covered here, please call the StemX team at 888-238-2468. StemX is located in Solana Beach, San Diego County, CA and in Laguna Woods, Orange County, CA.
Recent Posts

BMI and Weight Loss: Understanding the Impact on Health
Body Mass Index (BMI) serves as a widely used tool for assessing weight status relative to height, offering valuable insights

Five Habits that Could Be Worsening Your Knee Pain
Five Habits that Could Be Worsening Your Knee Pain

Regenerative Medicine Treatments for Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow
Overuse and repetitive contractions of the muscles and tendons of the forearm ...
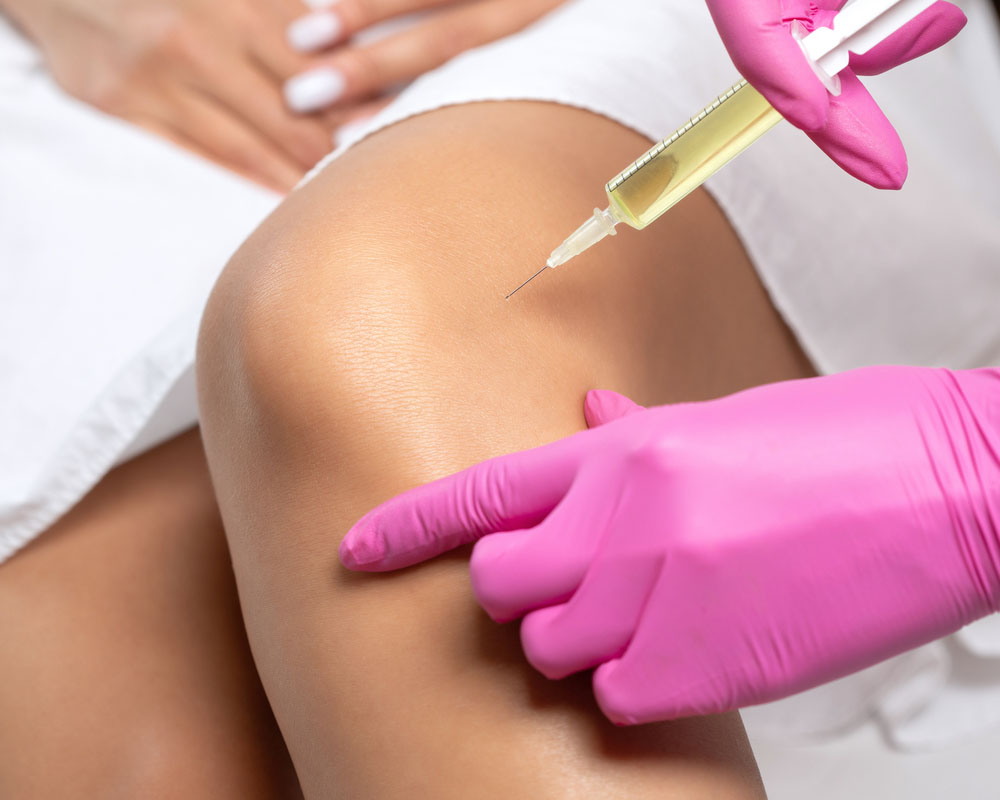
Cortisone Shots vs Regenerative Medicine Injections
Conventional treatments for joint pain often end up with long-term administration of cortisone shots, a powerful corticosteroid



