What Is Osteoarthritis Of The Knee?
Osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee is a progressive condition that causes aching pain, stiffness, and loss of mobility in the knee. Because OA is a degenerative disease due to wear and tear of the joint cartilage, symptoms gradually worsen.
Musculoskeletal joint conditions are extremely prevalent in the US. Osteoarthritis is the most common of the dozens of forms of arthritis. OA can affect any joint but is extremely prevalent in the knees.
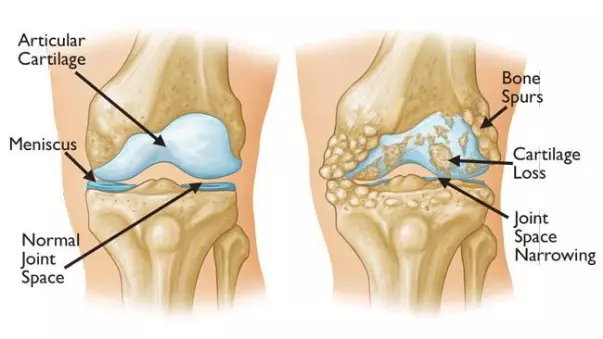
The knee being the largest joint in the body is also one of the strongest (See Figure 1). It's composed of three bones: the bottom part of the thighbone (the femur); the top part of the shinbone (tibia); and a large, round bone that covers and protects the joint (the patella or kneecap). The ends of these bones are lined in a smooth protective material called articular cartilage that acts like a shock absorber and helps the bones to move easily past each other while the body is in motion.
Figure 1. Depiction of a normal knee joint. Note the amount of joint space and smooth surface of the articular cartilage in the normal knee. (right) Depiction of osteoarthritic knee with articular cartilage loss, bone spurs, and narrowing of the joint space.
Causes, Signs And Symptoms
What causes knee osteoarthritis?The ultimate cause of knee pain and other osteoarthritis symptoms is often bone-on-bone friction as the cartilage begins to erode (See Figure 2). Over time, cartilage may wear away completely, leaving the joint vulnerable to permanent damage.
Phases Of Osteoarthritic Knee Degeneration
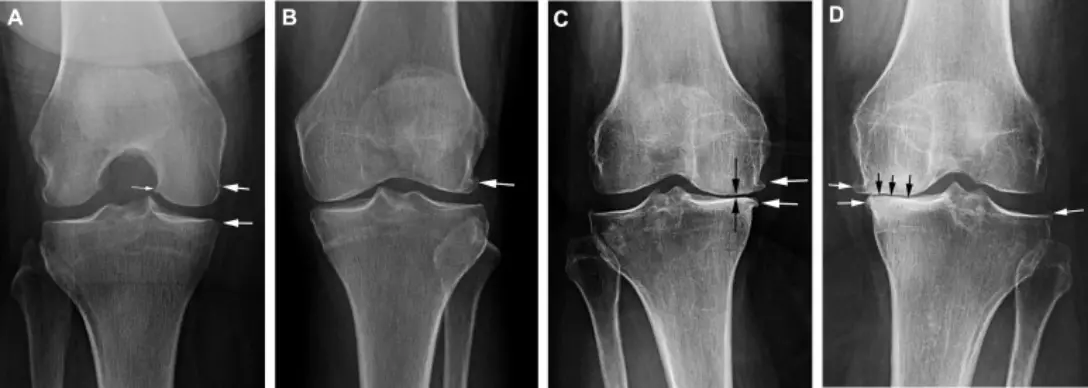
Figure 2. Phases of Osteoarthritic Knee Degeneration (knee osteoarthritis pictures).
(A) Black arrows point to the joint space between the femur and tibia in a healthy knee.
(B) Osteophyte formation is denoted by the white arrow marking the beginning of clinically graded osteoarthritis.
(C) Joint space gradually lessens with disease progression ultimately leading to D) a near complete loss of joint space in severe osteoarthritis, denoted by black arrows.
Pain from Knee OA may be experienced as a dull chronic pain that worsens after activity. In severe cases, the pain may become debilitating, limiting mobility, and preventing normal daily activities.
Patients with arthritis in the knee may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Joint pain, bone on bone knee pain
- Swollen knee, redness
- Stiffness
- Instability
- Immobility
- Crepitus (crackling, popping, or squeaking sounds emanating from the joint)
Age is the biggest risk factor for OA which is most common in adults 50 years and older, although trauma to the joint due to accidents or sports injuries are also significant risk factors across age groups.
The following are the major risk factors for knee osteoarthritis:
- Age. Years of wear and tear in addition to changes in the cells and extracellular matrix of joint tissues that occur with aging increase the susceptibility of an older adult to OA.
- Sex. Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis, this may be due to age-related nutritional deficiencies and/or hormonal changes.
- Obesity. Being overweight places excess burden on the body's joints and may increase the pace of cartilage degeneration.
- Repeated stress on the joint. Repetitive activities involving the knee can lead to more wear and tear. Athletes and those whose job activities require repetitive movements often suffer from OA.
- Genetics. There is a higher risk of developing OA if it runs in the family.
- Bone deformities. Misaligned joints due to abnormal bone structure increase the stress at the joint and may contribute to OA.
- Metabolic diseases. Changes in the mineral content and health of the tissues and bone in the knee joint increases the risk for OA.
Patients are seen in our California-based clinic where our specialists will base their diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis using a multipronged approach:
- Medical History: Our doctors will ask you about the nature of your knee pain (e.g., when and under what conditions you experience knee pain). They will ask about prior surgeries, accidents, and trauma to the knee.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will check for signs of trauma by testing the range of motion and listening for any cracking or popping noises (crepitus) or tenderness/pain, bruising, and swelling.
- X-rays/Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): X-rays provide clear, detailed images of the knee joint and may reveal bone spurs or narrowing of the joint, the classic hallmark for diagnosing osteoarthritis of the knee. Sometimes MRIs will be required to determine the extent of damage to the knee.
- Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves can create real-time images to assess the degree of inflammation or accumulation of fluid around the joint. Fluid can be tested to rule out other diseases (e.g., gout, rheumatoid arthritis in knee cap, or infections).
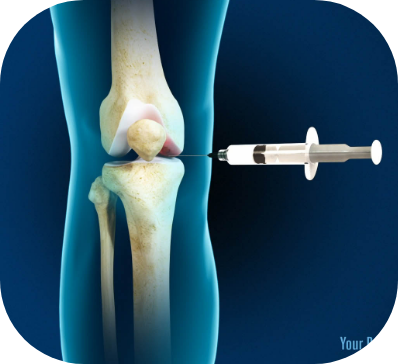
Treatment Options
The StemX clinic offers a range of customized Regenerative Medicine treatments to treat orthopedic injuries.
The StemX Approach
StemX is California's leading provider of holistic and regenerative medicine services. Our experts don't just offer popular treatments, but customized medical solutions based on individual needs.
Located in Solana Beach, California, the StemX clinic is composed of a team of expert doctors with years of experience administering regenerative medicine treatments for joint disease. Our team has:
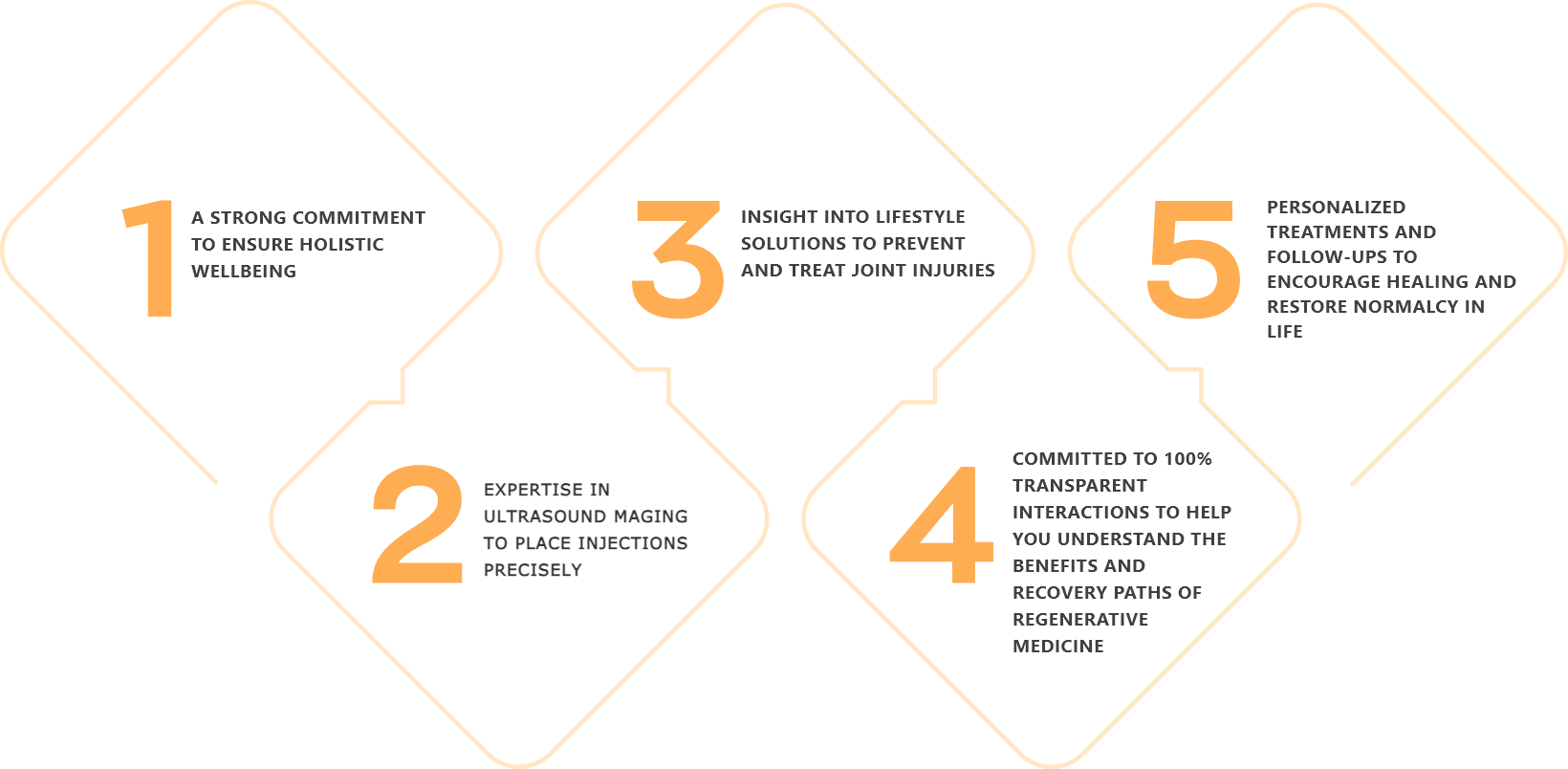





How To Get Started
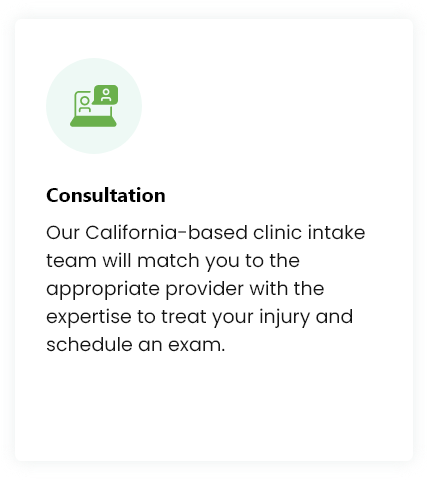
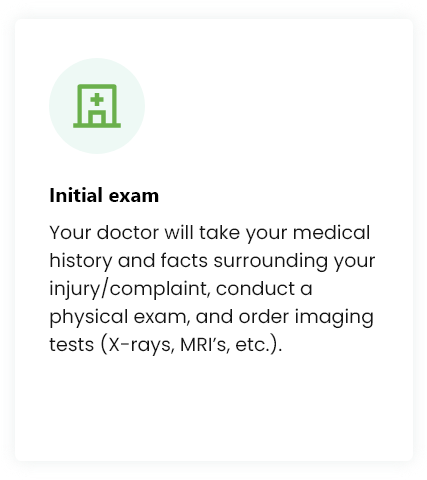
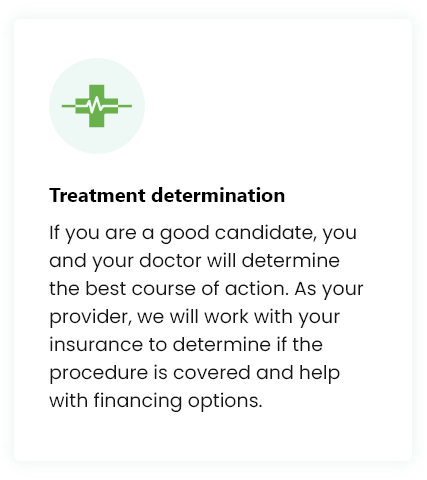
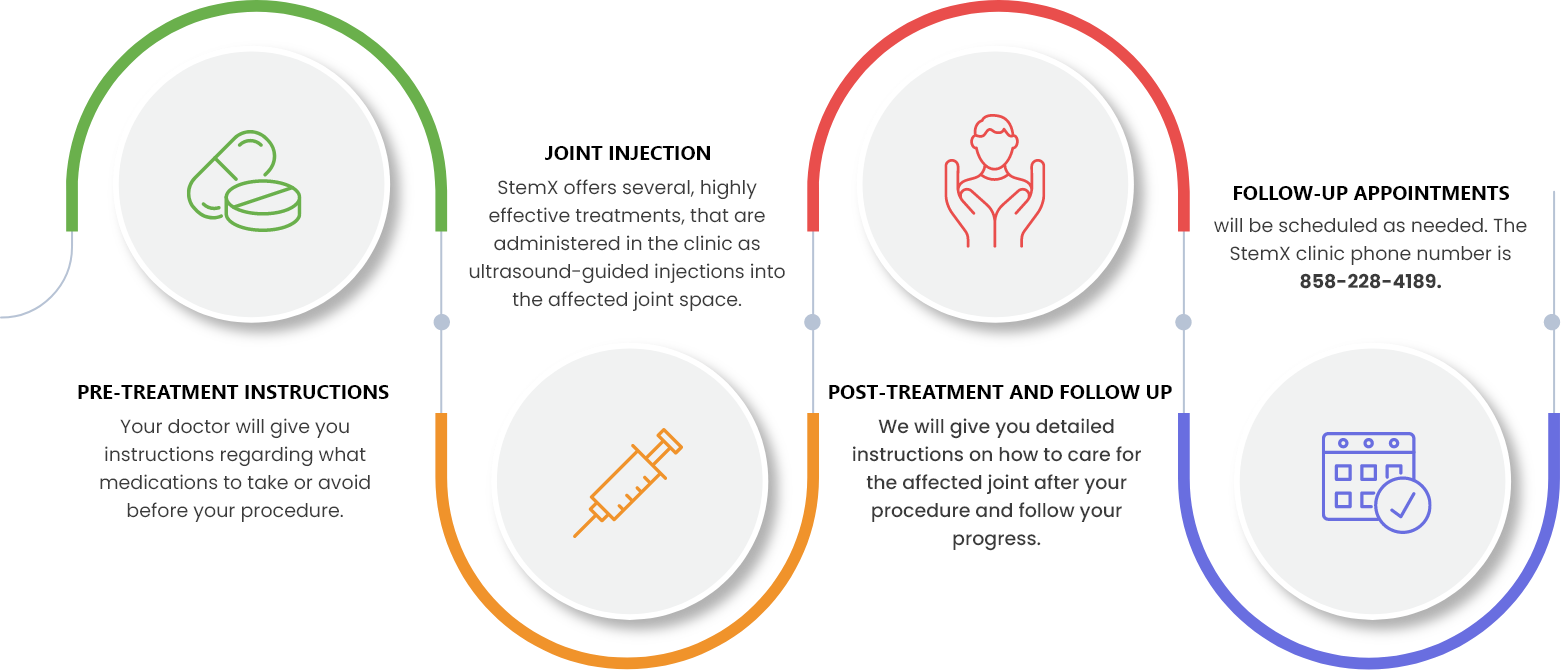
Treatment Procedure
While each treatment may be customized, you can expect your experience to be similar to the following:




All procedures are conducted in our Solana Beach, California clinic. 124 Lomas Santa Fe Dr #206, Solana Beach, CA 92075.
Frequently Asked Questions
Knee pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis in the knee, making it painful to jog, run, climb stairs or kneel. Stiff or swollen knees are common. OA can change the shape of the knee joint, making the knee feel unstable or wobbly.
There is no cure for arthritis of the knee. It's a lifelong condition. But the good news is treatment can relieve some of the symptoms. Treatment might even slow down or stop the disease from getting worse.
There are many signs and symptoms of arthritis of the knee: Creaking, clicking, grinding or snapping noises (crepitus). Difficulty walking. Joint pain that changes (gets better or worse) depending on the weather or activity.
Regenerative medicine treatments stimulate healing and reduce pain and inflammation with no side effects. NSAIDS and steroids reduce inflammation and pain but can have significant side effects and do not heal the condition.
Regenerative medicine treatments like Wharton's Jelly, amniotic fluid allografts, growth factors, and PRP along with physical therapy are all treatments used for knee OA. Regenerative medicine is long lasting with no side effects.
Living with knee OA is possible using regenerative medicine approaches. Some severe conditions may require surgery, however. Patients can often avoid surgery with regenerative medicine and activity modification.
Yes! Many studies have proven that Regenerative Medicine works even better in the long term than steroid injections or NSAIDS for severe arthritis in knee.
Regenerative medicine for knee pain includes Wharton's Jelly, amniotic fluid allografts, growth factors, and PRP. They are natural treatments with no side effects that stimulate healing and the growth of healthy tissue.
Up to 75% of StemX patients experience dramatically reduced pain and increased function. The option of regenerative medicine treatments is changing the landscape for patients suffering from common knee OA.
Treatments are not painful involving a simple injection done with a local anesthetic into the affected joint. Some soreness can be expected immediately after the procedure, but most patients experience little to no downtime.
Depending on the treatment, one can see improvement in as little as 3 weeks with maximum effects anywhere from 6-9 months later as the body is stimulated to heal.
Risk factors are minimal. Allergies to components of the injection or infection from injection are two possible risk factors but are very rare. Arthritis knee pain can be safely treated using regenerative medicine.
70% of patients are good candidates for regenerative medicine treatments. Surgery may be the only option for the most severe cases. Allergies, medication concerns, or implants that pose an infection risk may disqualify a patient from treatment.
Yes, cartilage producing chondrocyte cells can be stimulated to increase in number and thus repair damaged cartilage. However, cartilage cannot be regrown once completely gone.



